Announcements / November 8, 2024
Both current assets and current liabilities are listed on a company’s balance sheet. Let’s look at some examples of companies with high and low current ratios. You can find these numbers on a company’s balance sheet under total current assets and total current liabilities.
Current Assets
The current ratio may be more optimistic, while the acid test ratio gives a more conservative view of the company’s short-term financial position. The above analysis reveals that the two companies might actually have different liquidity positions even if both have the same current ratio number. While determining a company’s real short-term debt paying ability, an analyst should therefore not only focus on the current ratio figure but also consider the composition of current assets.
Company
One way they can speed up collections is by shortening credit terms. For instance, businesses can consider reducing the time customers have to pay from 60 days to 30 days. So, it’s normal for such companies to have slightly lower acid tax calculator return and refund estimator 2020 test ratios. On the other hand, tech companies (which don’t usually hold many physical products) will often aim for higher ratios. ” analyzed the complete transaction history of the Taiwan Stock Exchange between 1992 and 2006.
Get paid faster (improve accounts receivable)
The current ratio is one of the oldest ratios used in liquidity analysis. The current ratio is part of what you need to understand when investing in individual stocks, but those investing in mutual funds or exchange-trade funds needn’t worry about it. In general, a current ratio between 1.5 and 3 is considered healthy. Ratios lower than 1 usually indicate liquidity issues, while ratios over 3 can signal poor management of working capital. These include cash and short-term securities that your business can quickly sell and convert into cash, like treasury bills, short-term government bonds, and money market funds.
Free Course: Understanding Financial Statements
Current assets refers to the sum of all assets that will be used or turned to cash in the next year. Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. So, a ratio of 2.65 means that Sample Limited has more than enough cash to meet its immediate obligations.
Generally, the assumption is made that the higher the current ratio, the better the creditors’ position due to the higher probability that debts will be paid when due. It’s the most conservative measure of liquidity and, therefore, the most reliable, industry-neutral method of calculating it. A lower quick ratio could mean that you’re having liquidity problems, but it could just as easily mean that you’re good at collecting accounts receivable quickly.
If a company’s current ratio is less than one, it may have more bills to pay than easily accessible resources to pay those bills. Finally, the operating cash flow ratio compares a company’s active cash flow from operating activities (CFO) to its current liabilities. This allows a company to better gauge funding capabilities by omitting implications created by accounting entries. For example, a normal cycle for the company’s collections and payment processes may lead to a high current ratio as payments are received, but a low current ratio as those collections ebb. Another strategy is to focus on lowering the business’s current liabilities (bills they must pay in the short term). Companies can consider paying off short-term debts to improve their ratio immediately.
- A current ratio of less than 1.00 may seem alarming, but a single ratio doesn’t always offer a complete picture of a company’s finances.
- The current ratio provides the most information when it is used to compare companies of similar sizes within the same industry.
- This formula provides a straightforward way to gauge a company’s liquidity and its ability to meet short-term financial obligations.
- 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements.
- Your ability to pay them is called “liquidity,” and liquidity is one of the first things that accountants and investors will look at when assessing the health of your business.
- A strong Current Ratio can instill confidence in potential investors, but it should be evaluated alongside other financial metrics and the company’s specific circumstances.
However, an examination of the composition of current assets reveals that the total cash and debtors of Company X account for merely one-third of the total current assets. The current ratio or working capital ratio is a ratio of current assets to current liabilities within a business. However, special circumstances can affect the meaningfulness of the current ratio. For example, a financially healthy company could have an expensive one-time project that requires outlays of cash, say for emergency building improvements.
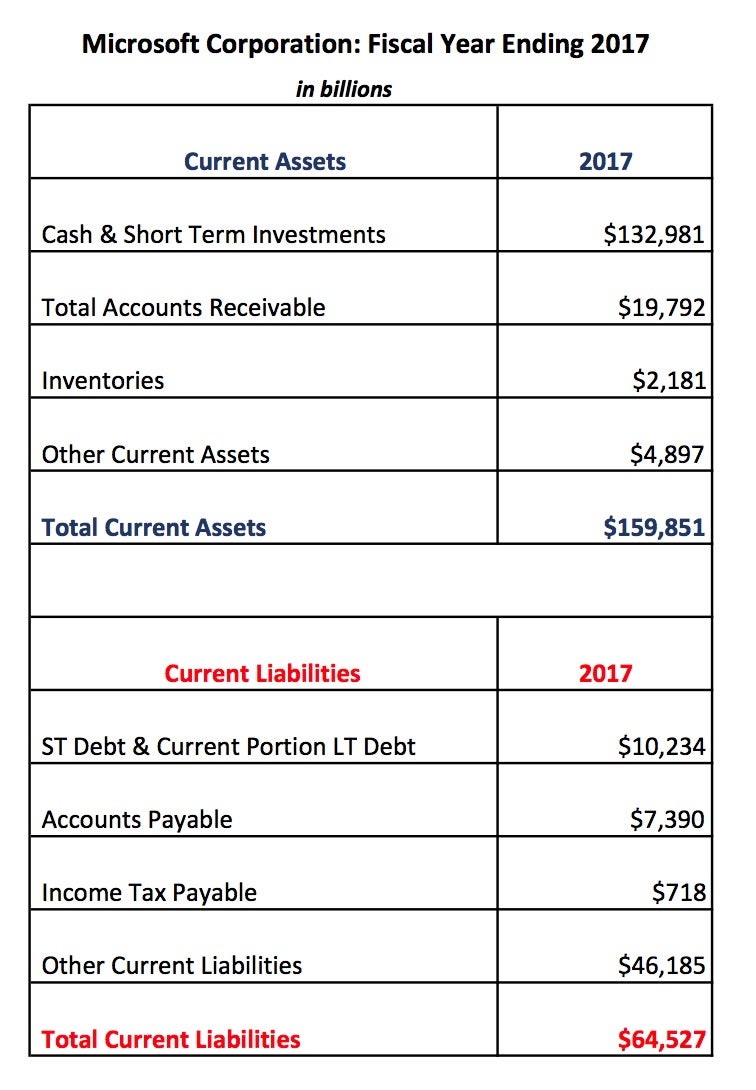
If a company is weighted down with a current debt, its cash flow will suffer. A higher current ratio is always more favorable than a lower current ratio because it shows the company can more easily make current debt payments. If all current liabilities of Apple had been immediately due at the end of 2021, the company could have paid all of its bills without leveraging long-term assets. To see how current ratio can change over time, and why a temporarily lower current ratio might not bother investors or analysts, let’s look at the balance sheet for Apple Inc. The quicker businesses can collect money customers owe them, the more cash they will have on hand.
A company with a current ratio of less than one doesn’t have enough current assets to cover its current financial obligations. XYZ Inc.’s current ratio is 0.68, which may indicate liquidity problems. The current ratio is a liquidity and efficiency ratio that measures a firm’s ability to pay off its short-term liabilities with its current assets. The current ratio is an important measure of liquidity because short-term liabilities are due within the next year. To calculate the ratio, analysts compare a company’s current assets to its current liabilities.